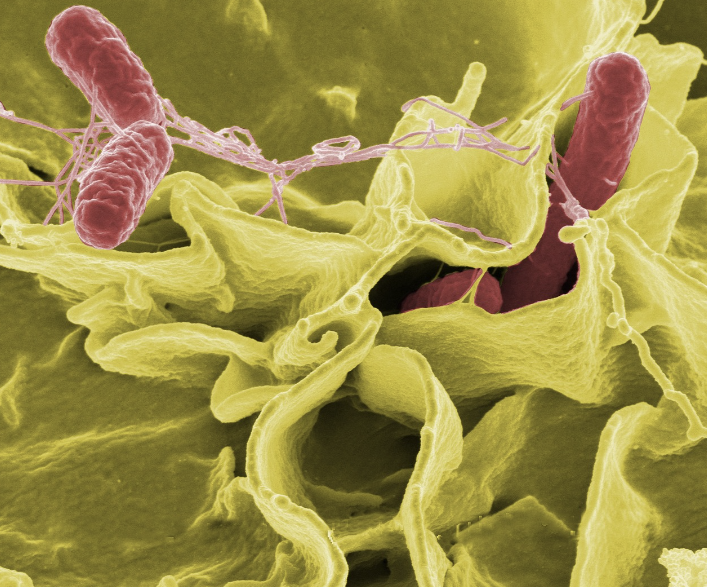
In today's discussion, we delve into the fascinating world of bacterial biofilms and explore their significant role in various aspects of our lives. The intricate structures formed by these communities of bacteria have garnered increasing attention from researchers and medical professionals alike, highlighting the importance of understanding their impact on health and the environment.
Exploring the Nature of Bacterial Biofilms
When considering bacterial biofilms, it is essential to recognize their complex nature and the ways in which they differ from free-floating bacteria. Biofilms consist of bacterial cells encased in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), providing them with protection and resilience against external factors. This matrix serves as a glue, allowing the bacteria to adhere to surfaces and form cohesive communities that are challenging to eradicate through conventional means.
Bacterial biofilms are ubiquitous in both natural and artificial environments. From dental plaque to slimy coatings on rocks in rivers, these structures can be found almost everywhere. While their presence may go unnoticed by the naked eye, their impact can be significant, leading to complications in various settings, including healthcare facilities, industrial processes, and even our homes.
The Medical Implications of Bacterial Biofilms
In the realm of medicine, bacterial biofilms pose a significant challenge due to their resistance to antibiotics and immune responses. Infections associated with biofilm formation, such as those found in chronic wounds, catheters, and medical implants, often prove difficult to treat effectively, leading to prolonged illness and increased healthcare costs. Understanding the mechanisms behind biofilm formation and persistence is crucial for developing novel strategies to combat these resilient bacterial communities.
Moreover, the presence of biofilms in medical settings can contribute to the spread of nosocomial infections, putting vulnerable individuals at risk. Hospitals and healthcare facilities must implement stringent protocols for biofilm prevention and removal to ensure patient safety and prevent outbreaks of drug-resistant pathogens. By raising awareness of the dangers associated with biofilm-related infections, we can take proactive measures to mitigate their impact on public health.
Environmental Impacts of Bacterial Biofilms
Beyond the realm of healthcare, bacterial biofilms also play a vital role in shaping ecosystems and environmental processes. In aquatic environments, biofilms serve as the foundation of food webs, providing nutrients and shelter for various organisms. They contribute to nutrient cycling and water quality maintenance, highlighting their ecological importance in maintaining balance within ecosystems.
However, the presence of biofilms can also have detrimental effects, particularly in industrial settings where they can cause biofouling and corrosion. The accumulation of biofilms in pipelines, water treatment systems, and industrial equipment can lead to decreased efficiency, increased maintenance costs, and potential system failures. By understanding the factors that promote biofilm growth, industries can implement preventive measures to mitigate these issues and ensure operational integrity.
Strategies for Controlling Bacterial Biofilms
Given the challenges posed by bacterial biofilms, researchers are actively exploring new strategies to control their formation and persistence. One approach involves disrupting the communication signals that allow bacteria to coordinate biofilm growth, a process known as quorum sensing inhibition. By targeting these signaling pathways, it may be possible to prevent biofilm formation or enhance the effectiveness of antimicrobial treatments.
Another promising avenue for biofilm control is the development of antimicrobial coatings and materials that prevent bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation on surfaces. By designing surfaces with specific properties that repel bacteria or inhibit their growth, researchers aim to create environments that are resistant to biofilm colonization, reducing the risk of infections and contamination in various settings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bacterial biofilms represent a complex and multifaceted phenomenon with far-reaching implications for human health, environmental sustainability, and industrial processes. By gaining a deeper understanding of the mechanisms underlying biofilm formation and persistence, we can develop effective strategies to control and mitigate their impact in diverse contexts. Through collaborative research efforts and innovative approaches, we can harness the power of knowledge to address the challenges posed by bacterial biofilms and pave the way for a healthier, more sustainable future.